In this post, we will explain how to set ulimit and file descriptors limit in Linux.
Challenges like number of open files in any of the production environment has become common now a day. Since many applications which are Java based and Apache based, are getting installed and configured, which may lead to too many open files, file descriptors etc. If this exceeds the default limit that is set, then one may face access control problems and file opening challenges. Many production environments come to standstill kind of situations because of this.
Luckily, we have “ulimit” command in any of the Linux based server, by which one can see/set/get number of files open status/configuration details. This command is equipped with many options and with this combination one can set number of open files. Following are step-by-step commands with examples explained in detail.
View Current Open File Limit in Linux
To get open file limit on any Linux server, execute the following command,
[root@ubuntu ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 146013
The above number shows that user can open ‘146013’ file per user login session.
[root@centos ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 149219 [root@debian ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 73906
This clearly indicates that individual Linux operating systems have different number of open files. This is based on dependencies and applications which are running in respective systems.
ulimit command
As the name suggests, ulimit (user limit) is used to display and set resources limit for logged in user.When we run ulimit command with -a option then it will print all resources’ limit for the logged in user. Now let’s run “ulimit -a” on Ubuntu / Debian and RHEL systems,
Ubuntu / Debian System,
shashi@Ubuntu ~}$ ulimit -a core file size (blocks, -c) 0 data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited scheduling priority (-e) 0 file size (blocks, -f) unlimited pending signals (-i) 5731 max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64 max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited open files (-n) 1024 pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8 POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200 real-time priority (-r) 0 stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192 cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited max user processes (-u) 5731 virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited file locks (-x) unlimited
RHEL /CentOS System
shashi@centos ~}$ ulimit -a core file size (blocks, -c) 0 data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited scheduling priority (-e) 0 file size (blocks, -f) unlimited pending signals (-i) 5901 max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64 max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited open files (-n) 1024 pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8 POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200 real-time priority (-r) 0 stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192 cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited max user processes (-u) 5901 virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited file locks (-x) unlimited
As we can be seen here different OS have different limits set. All these limits can be configured/changed using “ulimit” command.
To display the individual resource limit then pass the individual parameter in ulimit command, some of parameters are listed below:
- ulimit -n –> It will display number of open files limit
- ulimit -c –> It display the size of core file
- umilit -u –> It will display the maximum user process limit for the logged in user.
- ulimit -f –> It will display the maximum file size that the user can have.
- umilit -m –> It will display the maximum memory size for logged in user.
- ulimit -v –> It will display the maximum memory size limit
Use below commands check hard and soft limits for number of open file for the logged in user
shashi@Ubuntu ~}$ ulimit -Hn 1048576 shashi@Ubuntu ~}$ ulimit -Sn 1024
How to fix the problem when limit on number of maximum files was reached ?
Let’s assume our Linux server has reached the limit of maximum number of open files and want to extend that limit system wide, for example we want to set 100000 as limit of number of open files.
Use sysctl command to pass fs.file-max parameter to kernel on the fly, execute beneath command as root user,
root@ubuntu~]# sysctl -w fs.file-max=100000 fs.file-max = 100000
Above changes will be active until the next reboot, so to make these changes persistent across the reboot, edit the file /etc/sysctl.conf and add same parameter,
root@ubuntu~]# vi /etc/sysctl.conf fs.file-max = 100000
save and exit file,
Run the beneath command to make above changes into effect immediately without logout and reboot.
root@ubuntu~]# sysctl -p
Now verify whether new changes are in effect or not.
root@ubuntu~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 100000
Use below command to find out how many file descriptors are currently being utilized:
[root@ansible ~]# more /proc/sys/fs/file-nr 1216 0 100000
Note: Command “sysctl -p” is used to commit the changes without reboot and logout.
Set ulimit (User level resource limit) via limit.conf file
“/etc/sysctl.conf” file is used to set resource limit system wide but if you want to set resource limit for specific user like Oracle, MariaDB and Apache then this can be achieved via “/etc/security/limits.conf” file.
Sample limit.conf is shown below,
root@ubuntu~]# cat /etc/security/limits.conf
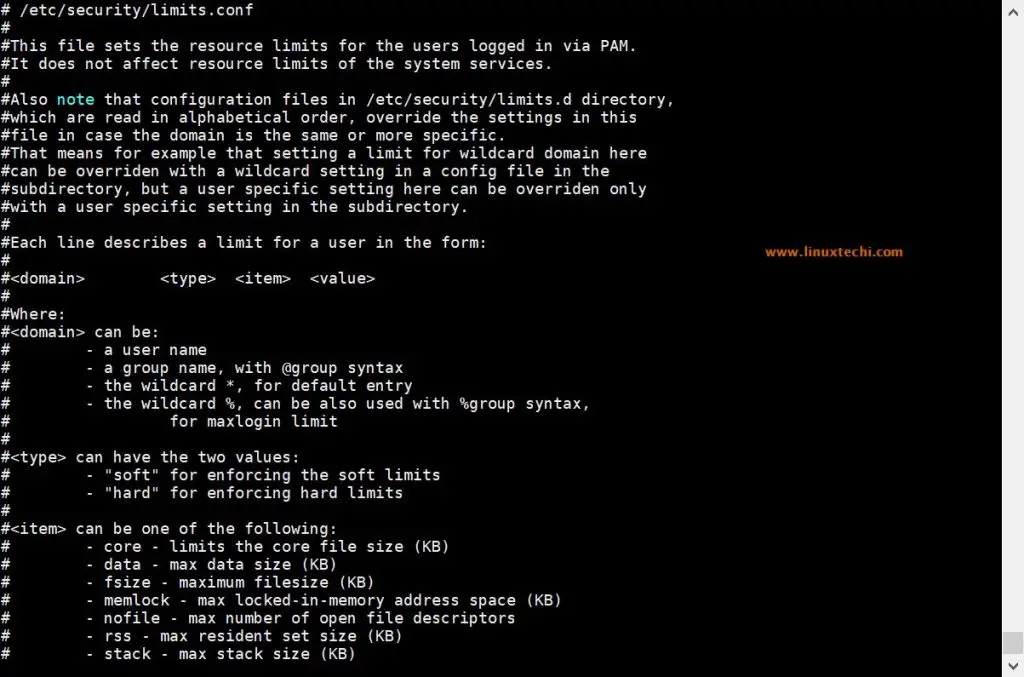
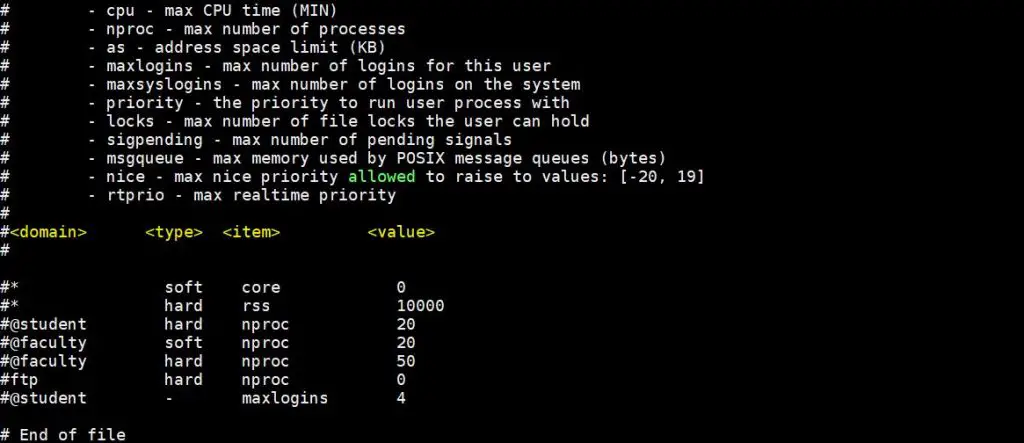
Let’s assume we want to set hard and soft limit on number of open files for linuxtechi user and for oracle user set hard and soft limit on number of open process, edit the file “/etc/security/limits.conf” and add the following lines
# hard limit for max opened files for linuxtechi user linuxtechi hard nofile 4096 # soft limit for max opened files for linuxtechi user linuxtechi soft nofile 1024 # hard limit for max number of process for oracle user oracle hard nproc 8096 # soft limit for max number of process for oracle user oracle soft nproc 4096
Save & exit the file.
Note: In case you want to put resource limit on a group instead of users, then it can also be possible via limit.conf file, in place of user name , type @<Group_Name> and rest of the items will be same, example is shown below,
# hard limit for max opened files for sysadmin group @sysadmin hard nofile 4096 # soft limit for max opened files for sysadmin group @sysadmin soft nofile 1024
Verify whether new changes are in effect or not,
~]# su - linuxtechi ~]$ ulimit -n -H 4096 ~]$ ulimit -n -S 1024 ~]# su - oracle ~]$ ulimit -H -u 8096 ~]$ ulimit -S -u 4096
Note: Other majorly used command is “lsof” which is used for finding out “how many files are opened currently”. This command is very helpful for admins.
Conclusion
As mentioned in the introduction section “ulimit” command is very powerful and helps one to configure and make sure application installations are smoother without any bottlenecks. This command helps in fixing many of the number of file limitations in Linux based servers.

cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max shows 146013, but
ulimit -a shows:
open files (-n) 1024
What is the difference
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max –> shows the limit of max open file for the system wide
ulimit -a –> will show all the resources limit of a specific user
hello, ok so do you mean that if I set a value like this it will be add to limits.conf?
ulimit -f 65000
Hi David,
User level limits are configured via ‘/etc/security/limits.conf’ file. Example is shown in above guide.