In this blog post, we will learn how to run Linux commands within vi/vim editor and make the most of this powerful feature.
The vi or vim editor is one of the most popular text editors in the Linux world, revered for its power and flexibility. One of its lesser-known but highly useful features is the ability to run Linux commands directly from within the editor. This can save time and streamline your workflow, especially when editing configuration files or scripts.
There are some scenarios where system admin wants to run Linux commands and insert the output of commands in vi editor without leaving it. This can be possible, let’s see with the below examples.
1) Running a Single Command
First Go to command mode in vi editor by pressing ‘esc‘ key and then type “:“, followed by “!” and the command, example is shown below.
:!Linux_Command
Example: Run the ifconfig command within the /etc/hosts file.
$ sudo vi /etc/hosts
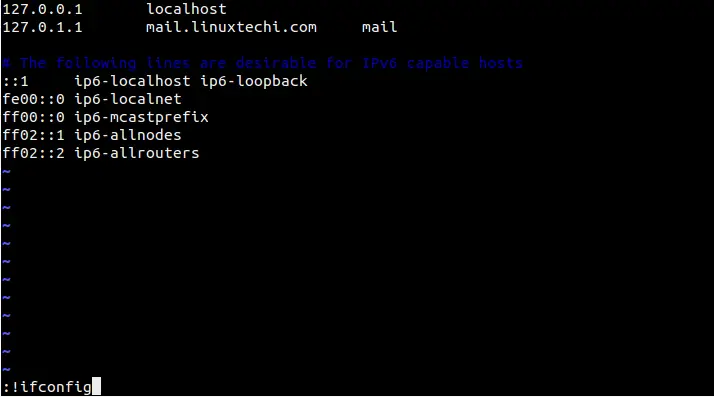
2) Insert Command Output in vi editor
Sometimes, you may want to run a command and insert its output directly into your file. This can be handy when you need to include system information or the contents of another file.
So, to insert the output of a UNIX or Linux command into a file, refer the following steps:
- Move the cursor to the location where you want to insert the output.
- Press Esc to ensure you are in normal mode.
- Type the following command:
:r!command
Example: Insert the output of hostname in /etc/hosts file.
$ sudo vi /etc/hosts
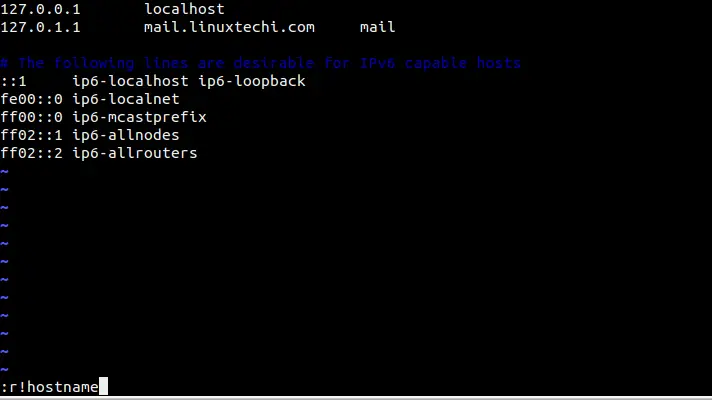
When we press enter , the output of hostname command will be inserted in the file just after the cursor position.
3) Starting a shell within vi Editor
We can start the shell (bash or sh) within the editor , to start a shell use below command :
:<Shell>
Type of a shell that is started is determined by the $SHELL variable. And to return back to editor use exit or Ctrl-D
Example : Start sh shell in vi editor
$ sudo vi /etc/hosts
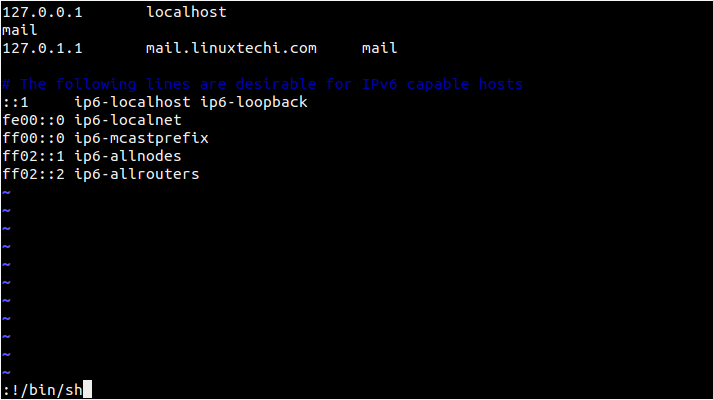
Note: Above discussed features becomes very useful if you are using vi/vim to document a UNIX command and you wanted to include examples of the output from this command.
4) Open an existing file within the vi editor
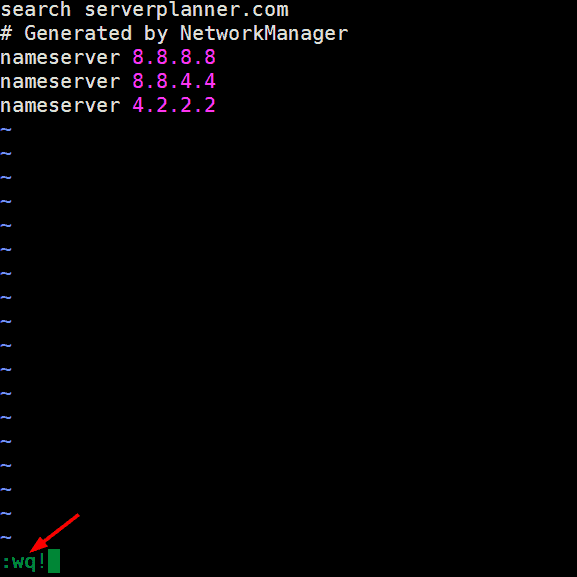
Let’s assume we have opened /etc/hosts file using vi editor and want to open and edit /etc/resolv.conf without leaving the vi editor, this can be done by using below syntax in the command mode,
:e<file-to-be-edited>
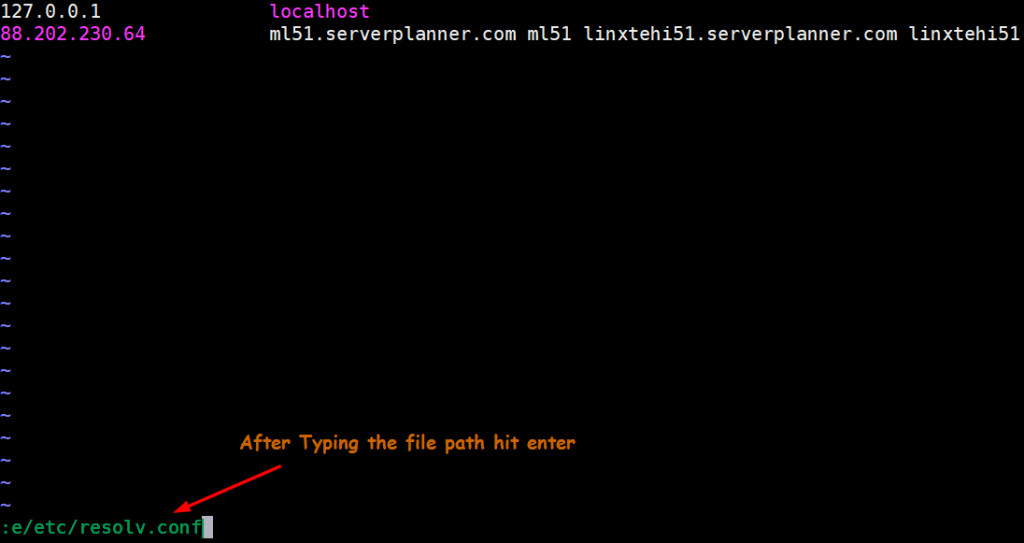
Once we hit enter it will open /etc/resolv.conf file, do the change whatever you want and then save and exit the file.
5) Filtering Text through External Commands
We can also filter text through external commands using the ! operator in combination with visual mode.
Example: To sort a list of words alphabetically
- Highlight the lines you want to sort by entering visual mode with V and moving the cursor to select the text.
- Press :
- Type the following command:
- !sort
- Press Enter.
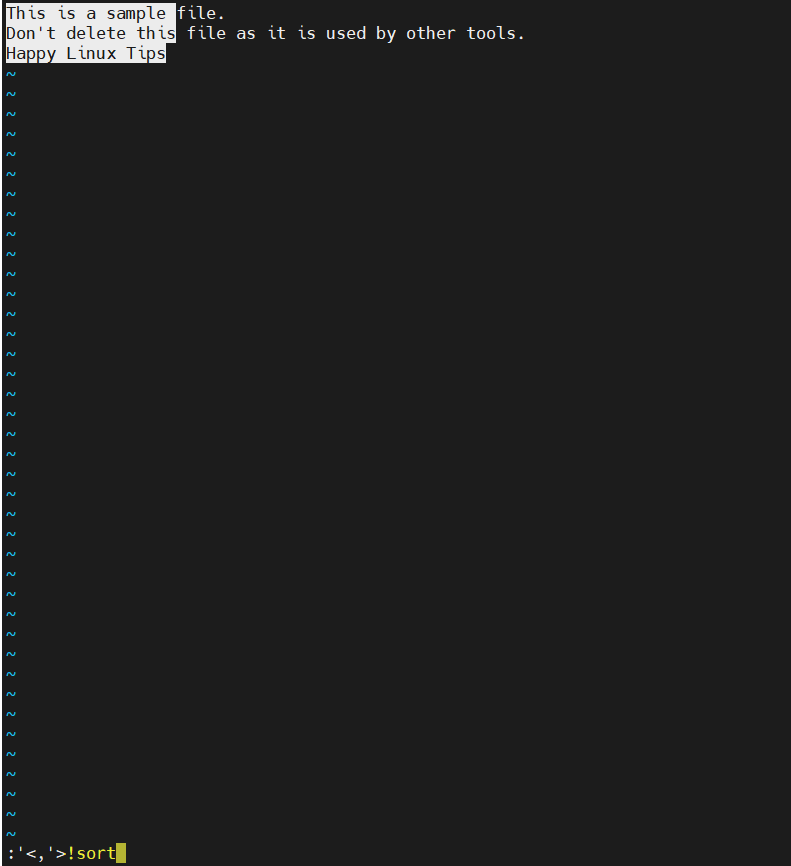
The selected lines will be sorted alphabetically and replaced in the file.
That’s all from this post, I hope these tips will help you to work on vi and vim editor more efficiently. Feel free to post your queries and feedback in below comments section.
Also Read: 16 IP Command Examples in Linux



You can filter lines through a shell command. For example, to sort some lines:
Go the the top of the lines and press: ma
Go to the bottom of the lines and press: !’asort
and then RETURN.
The lines will be sorted. 🙂