In this tutorial, we will cover how to enable proxy settings for Yum/DNF command.
In most of the data centers, internet access is restricted for Unix (or Linux) and Windows servers. This means downloads must be routed through proxy servers. For Linux servers based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), Fedora, Rocky Linux, and Alma Linux, using a proxy server is necessary to install software packages and updates (patches) with the yum or dnf command when a direct internet connection is unavailable.
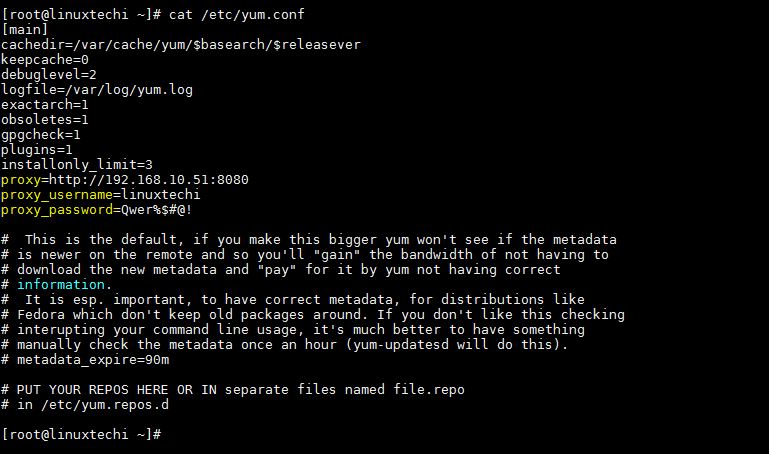
Proxy settings for Yum/DNF command can be configure using variables in /etc/yum.conf file. Under main section define the proxy settings like below:
[main] ……………… proxy=http://<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy_Port> proxy_username=<Proxy-User-Name> proxy_password=<Proxy-Password> ………………
Save and exit the file and start using the yum command. Sample yum Config file with proxy settings is shown below :
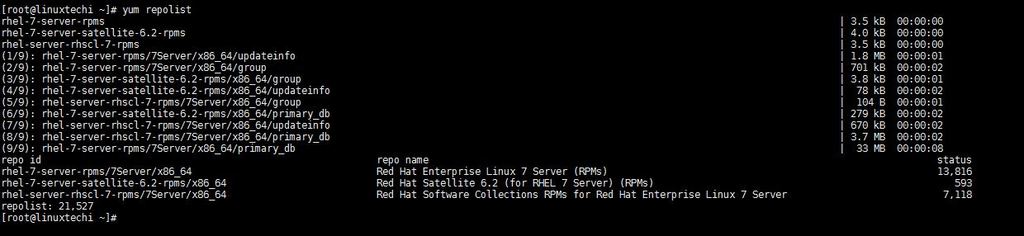
Just for the verification you can run beneath command to see whether you are able to fetch the packages or not.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# yum repolist
Alternate way to configure proxy settings for Yum or DNF command
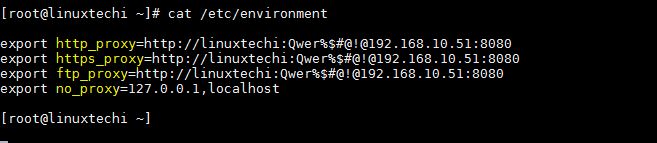
Yum or DNF proxy settings can also be configure via variables in the file “/etc/environment“. Example is shown below:
.....................................................................
http_proxy=http://{Proxy-User-Name}:{Proxy-Password}@<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy-Port>
https_proxy= http://{Proxy-User-Name}:{Proxy-Password}@<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy-Port>
ftp_proxy= http://{Proxy-User-Name}:{Proxy-Password}@<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy-Port>
no_proxy=127.0.0.1,localhost
...................................................................
# source /etc/environment
Above proxy settings will be applicable system wide.
Defining proxy settings for Yum/DNF using “/root/.bashrc“, set the following variables
export http_proxy=http://{Proxy-User-Name}:{Proxy-Password}@<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy-Port>
export https_proxy= http://{Proxy-User-Name}:{Proxy-Password}@<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy-Port>
export ftp_proxy= http://{Proxy-User-Name}:{Proxy-Password}@<Proxy-Server-IP-Address>:<Proxy-Port>
export no_proxy=127.0.0.1,localhost
To activate above variables, run
# source /root/.bashrc
Also Read: How to Set Proxy Settings for APT Command


Hi,
Thanks for your help, but I still have a bad issue when I try to execute yum.
I configure my /etc/environment like you, try “yum update”
and now, (as always, before my configuration), I have this error :
There was an error communicating with RHN.
Red Hat Satellite or RHN Classic support will be disabled.
Error communicating with server. The message was:
Unable to connect to the host and port specified
[a874878adm@sma6333 etc]$
Hi Juliette,
First set the proxy variables on the terminal and then try executing the commands, If you wan to use ‘/etc/environment’ file then you have to first source the file using the command:
# source /etc/environment
Best tutorial out there. Thank you
Hi, My CentOS Server is running on virtualbox, I run privoxy and make a http proxy on port 8118, then set the proxy in yum.conf file like this:
proxy=192.168.1.104:8118
This is my main OS ip, but I see “Connection refused …” errro
with foxyproxy on firefox I am connected with same details , please help
I’m not sure the ‘#’ in the password without escaping will be accepted by your system without commenting everything after.
In the /etc/environment or root/bash.rc examples how would you account for a domain designation such as “domainname\username”
http_proxy=http://domain\username:password@proxyaddress:80 does not seem to work.
In the yum.conf example it works because I can specify the username as a variable… Any advice would be greatly appreciated.
You can try to escape like that :
http_proxy=http://domain\\username:password@proxyaddress:80
http is working but https not working. Any idea ?
The file /etc/environment is a configuration file, not a bash initialization script, so you should not include “export” in these definitions