In this post, we will cover how to install VirtualBox on Fedora Linux step by step. At time of writing this post, virtualbox package is available only for Fedora 36, but this post will also be applicable for Fedora 38/37 when it’s package is released.
VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization software for x86 hardware. It is available for both Windows and Linux like operating system, it is one the most popular virtualization software used at Desktop level. It provides a Graphical User interface (GUI) through which we can create and manage virtual machines, apart from this we can also create Snapshots of VMs, Cloning of the VMs and can create our own customize network for the VMs.
Prerequisites
- Pre Installed Fedora 38/37/36
- Sudo User with admin rights
- Stable Internet connectivity
- At least 2GB of RAM
- At least Dual Core Processor
- 25 GB free disk space
Without any delay, let’s jump into VirtualBox installation steps,
1) Install VirtualBox Dependencies
Login to your fedora system and open the terminal and then run following dnf commands to install virtualbox dependencies.
$ sudo dnf -y install @development-tools $ sudo dnf install kernel-headers kernel-devel dkms -y
After installing all the dependecies, reboot your fedora system once using following command
$ sudo reboot
2) Enable VirtualBox Package Repository
Import public key for VirtualBox rpm, run
$ wget -q https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox.asc $ sudo rpm --import oracle_vbox.asc
Now, create Virtualbox package repository file under the folder ‘/etc/yum.repos.d/‘ with following content,
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/virtualbox.repo [VirtualBox] name=Fedora $releasever - $basearch - VirtualBox baseurl=http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/rpm/fedora/$releasever/$basearch enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox.asc
Save and exit the file.
3) Install latest VirtualBox
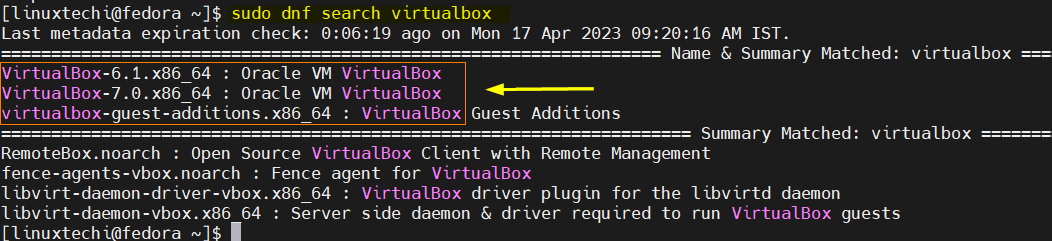
Before installing, we can view available virtualbox versions using following command,
$ sudo dnf search virtualbox
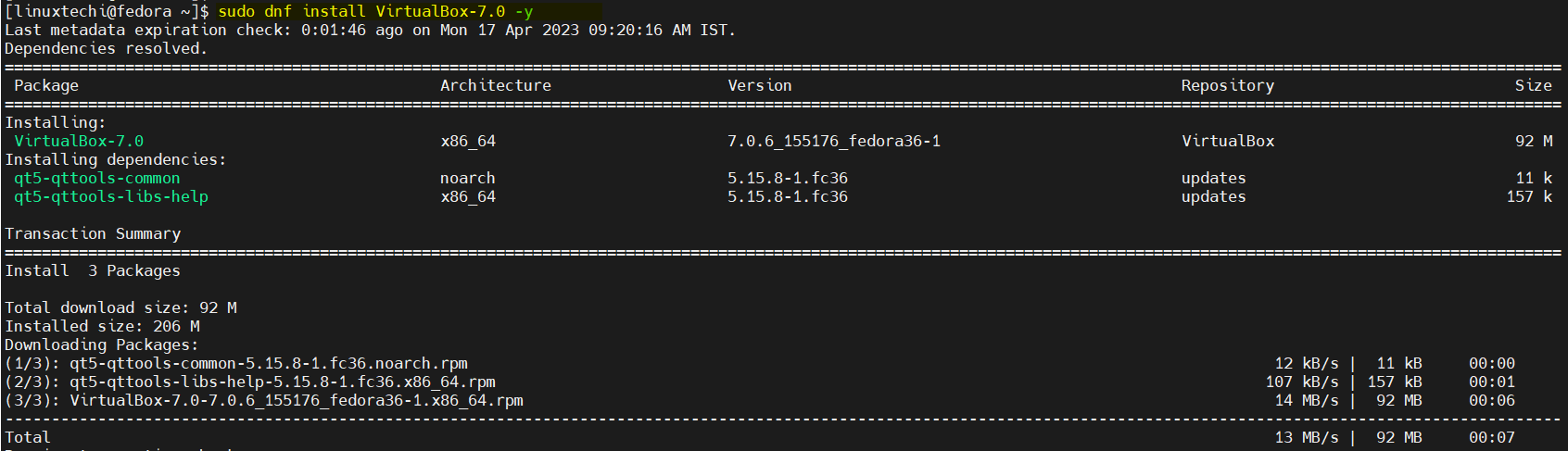
To install latest virtualbox 7 , run following dnf command,
$ sudo dnf install VirtualBox-7.0 -y
4) Add Local User to vboxusers Group
If you want your local user to manage or operate virtualbox without sudo then add your local user to the group ‘vboxusers’. Run following command,
$ sudo usermod -aG vboxusers $USER $ newgrp vboxusers $ $ id uid=1000(linuxtechi) gid=976(vboxusers) groups=976(vboxusers),10(wheel),1000(linuxtechi) context=unconfined_u:unconfined_r:unconfined_t:s0-s0:c0.c1023 $
5) Access VirtualBox Manager
To access virtualbox manager from your desktop environment, search virtualbox as shown below,
Click on VirtualBox icon,
Perfect, above screen confirms that we have successfully started VirtualBox manager.
6) Install VirtualBox Extension Pack
If you want to add additional functionalities to your virtualbox like support of USB 2.0/3.0, PXE boot, VirtualBox RDP and disk encryption then install extension pack.
Use below wget command to download extension pack for VirtualBox 7.0
$ wget https://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/7.0.6/Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-7.0.6a-155176.vbox-extpack
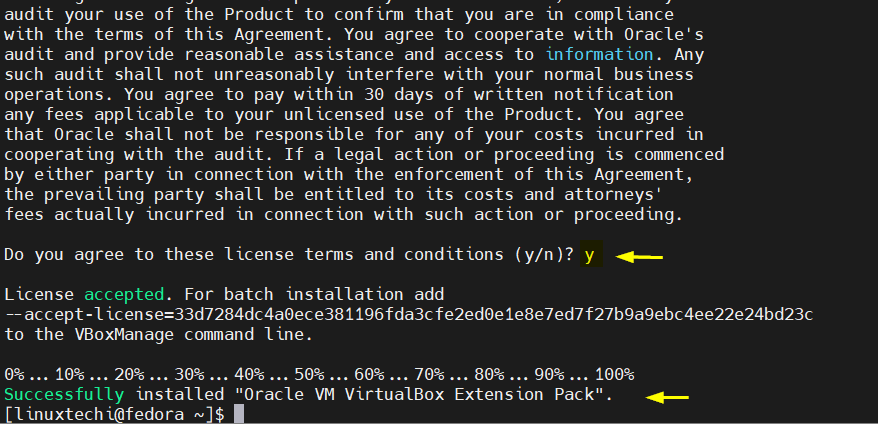
Install extension by running beneath command,
$ sudo VBoxManage extpack install Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-7.0.6a-155176.vbox-extpack
output,
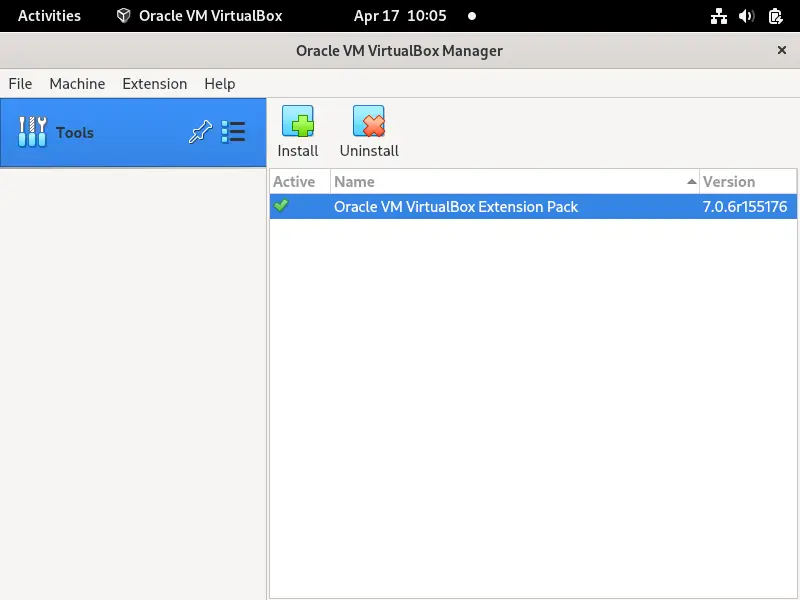
Above output confirms that extension pack has been installed successfully. Let’s verify from VirtualBox GUI,
File –> Tools –> Extension Pack Manager
Great, above screen confirms that Extension Pack Manager is installed and active. Now, you can start creating virtual machines.
That’s all from this post, I hope you have found it informative, kindly do post your queries and feedback in below comments section.



Excellent Article. Finally, I was able to install VirtualBox on CentOS 7. 🙂
I had a “Policy rejected asymmetric algorithm” problem on Fedora 38 and fixed just using “oracle_vbox_2016.asc” instead “oracle_vbox.asc”
after path 1) , virtualbox dependencies, and rebooting I just loose wifi interface and blootooth interface,
and if i add usb wifi dongle, it does not help.
It is a fresh new start with FEDORA 39.
Linux 6.5.6-300.fc39.x86_64
HOW DO I AVOID THE PROBLEM ?
Same problem here. I am on Fedora 40.
And I cannot revert it or fix it.
Any help?