A VNC (Virtual Network Computing) Server is a GUI based desktop sharing platform that allows you to access remote desktop machines. In Centos 8 and RHEL 8 systems, VNC servers are not installed by default and need to be installed manually. In this article, we’ll look at how to install VNC Server on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 systems with a simple step-by-step installation guide.
Prerequisites to Install VNC Server on Centos 8 / RHEL 8
To install VNC Server in your system, make sure you have the following requirements readily available on your system:
- CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
- GNOME Desktop Environment
- Root access
- DNF / YUM Package repositories
Step by Step Guide to Install VNC Server on Centos 8 / RHEL 8
Step 1) Install GNOME Desktop environment
Before installing VNC Server in your CentOS 8 / RHEL 8, make sure you have a desktop Environment (DE) installed. In case GNOME desktop is already installed or you have installed your server with gui option then you can skip this step.
In CentOS 8 / RHEL 8, GNOME is the default desktop environment. if you don’t have it in your system, install it using the following command:
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dnf groupinstall "workstation" Or [root@linuxtechi ~]# dnf groupinstall "Server with GUI"
Once the above packages are installed successfully then run the following command to enable the graphical mode
[root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl set-default graphical
Now reboot the system so that we get GNOME login screen.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# reboot
Once the system is rebooted successfully uncomment the line “WaylandEnable=false” from the file “/etc/gdm/custom.conf” so that remote desktop session request via vnc is handled by xorg of GNOME desktop in place of wayland display manager.
Note: Wayland is the default display manager (GDM) in GNOME and it not is configured to handled remote rendering API like X.org
VNC server will not work properly if SElinux is enabled on your system, as of now work around is to disable it using following commands,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# setenforce 0 [root@linuxtechi ~]# sed -i --follow-symlinks 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Step 2) Install VNC Server (tigervnc-server)
Next we’ll install the VNC Server, there are lot of VNC Servers available, and for installation purposes, we’ll be installing TigerVNC Server. It is one of the most popular VNC Server and a high-performance and platform-independent VNC that allows users to interact with remote machines easily.
Now install TigerVNC Server using the following command:
[root@linuxtechi ~]# dnf install tigervnc-server tigervnc-server-module -y
Step 3) Set VNC Password for Local User
Let’s assume we want ‘pkumar’ user to use VNC for remote desktop session, then switch to the user and set its password using vncpasswd command,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# su - pkumar [pkumar@linuxtechi ~]$ vncpasswd Password: Verify: Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n A view-only password is not used [pkumar@linuxtechi ~]$ [pkumar@linuxtechi ~]$ exit logout [root@linuxtechi ~]#
Step 4) Setup VNC Server Configuration File
Next step is to configure VNC Server Configuration file. Create a file “/etc/systemd/system/[email protected]” with the following content so that tigervnc-server’s service started for above local user “pkumar”.
[root@linuxtechi ~]# vim /etc/systemd/system/[email protected] [Unit] Description=Remote desktop service (VNC) After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l pkumar -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1280x1024" PIDFile=/home/pkumar/.vnc/%H%i.pid ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :' [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and exit the file,
Note: Replace the user name in above file which suits to your setup.
By default, VNC server listen on tcp port 5900+n, where n is the display number, if the display number is “1” then VNC server will listen its request on TCP port 5901.
Step 5) Start VNC Service and allow port in firewall
I am using display number as 1, so use the following commands to start and enable vnc service on display number “1”,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl daemon-reload [root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl start vncserver@:1.service [root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl enable vncserver@:1.service Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/vncserver@:1.service → /etc/systemd/system/[email protected]. [root@linuxtechi ~]#
Use below netstat or ss command to verify whether VNC server start listening its request on 5901,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# netstat -tunlp | grep 5901
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5901 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8169/Xvnc
tcp6 0 0 :::5901 :::* LISTEN 8169/Xvnc
[root@linuxtechi ~]# ss -tunlp | grep -i 5901
tcp LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:5901 0.0.0.0:* users:(("Xvnc",pid=8169,fd=6))
tcp LISTEN 0 5 [::]:5901 [::]:* users:(("Xvnc",pid=8169,fd=7))
[root@linuxtechi ~]#
Use below systemctl command to verify the status of VNC server,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# systemctl status vncserver@:1.service
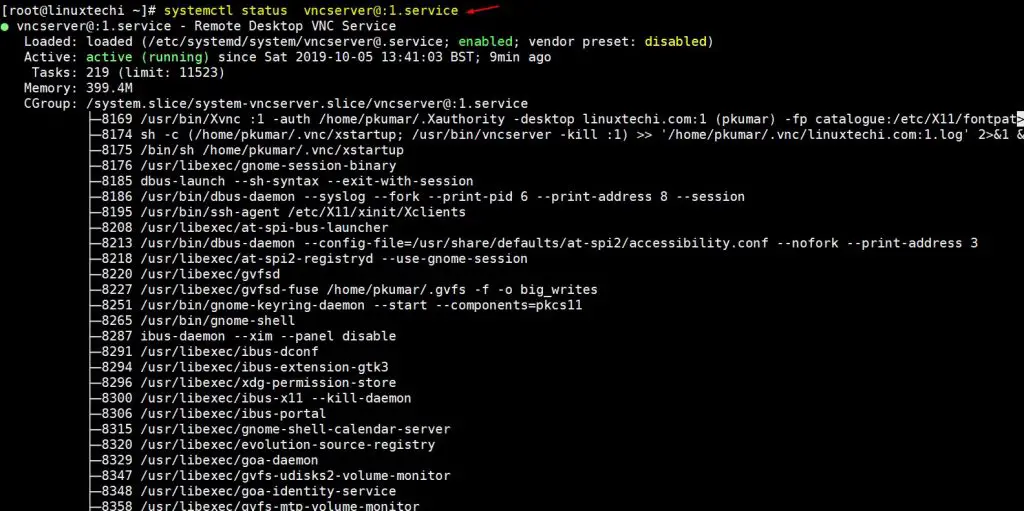
Above command’s output confirms that VNC is started successfully on port tcp port 5901. Use the following command allow VNC Server port “5901” in os firewall,
[root@linuxtechi ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5901/tcp success [root@linuxtechi ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success [root@linuxtechi ~]#
Step 6) Connect to Remote Desktop Session
Now we are all set to see if the remote desktop connection is working. To access the remote desktop, Start the VNC Viewer from your Windows / Linux workstation and enter your VNC server IP Address and Port Number and then hit enter
Next, it will ask for your VNC password. Enter the password that you have created earlier for your local user and click OK to continue
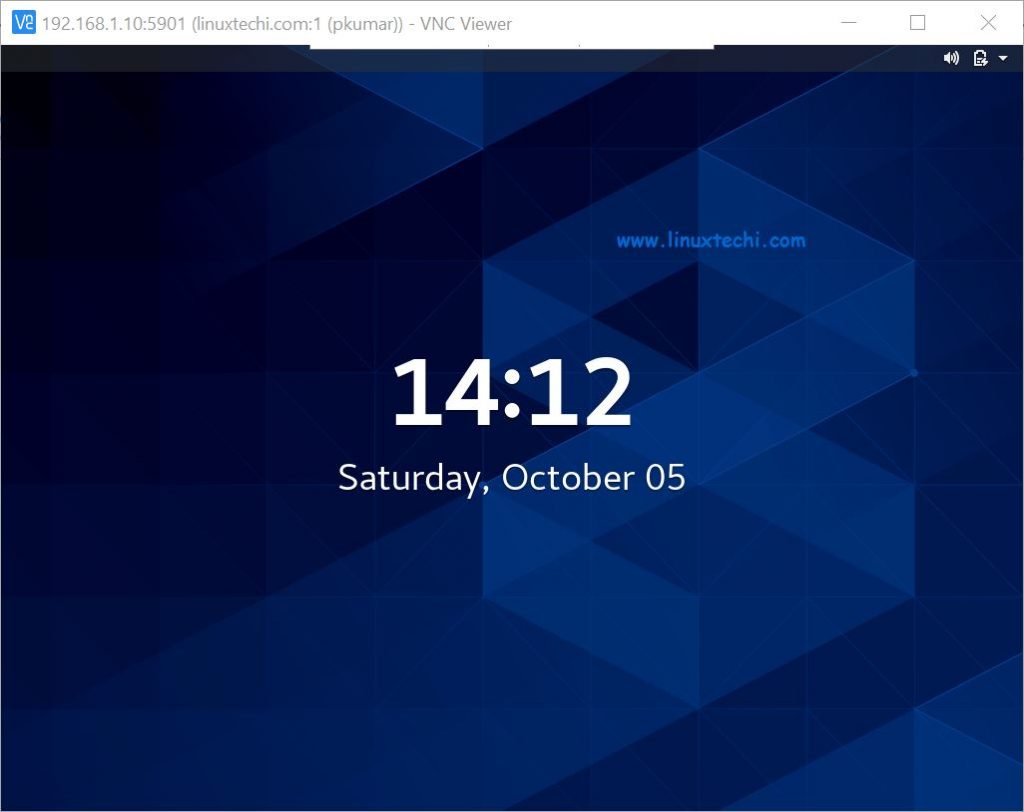
Now you can see the remote desktop,
That’s it, you’ve successfully installed VNC Server in Centos 8 / RHEL 8.
Conclusion
Hope the step-by-step guide to install VNC server on Centos 8 / RHEL 8 has provided you with all the information to easily setup VNC Server and access remote desktops. Please provide your comments and suggestion in the feedback section below. See you in the next article…Until then a big THANK YOU and BYE for now!!!
Read Also : How to Configure Rsyslog Server in CentOS 8 / RHEL 8



Hi, I followed your steps and the connection works. But when I hit software, e.g. for updates, it tells me I have not sufficent rights. And sometimes a window with SELinux pops up and tells me something about “GeoClue”… Those things never happen when I logon directly.
Regards
Hi Marc,
Try disabling the SELinux on your system using the following commands,
# setenforce 0
# sed -i –follow-symlinks ‘s/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g’ /etc/sysconfig/selinux
When I try to login I (tried with two different viewers) get an authentication error as soon as I type a single character in the password field (even though I have not pressed return). What am I doing wrong?
I am also wondering about the first password you have to enter – why do I have to enter that even though I must authenticate again? And what about if I define several users with different passwords – can I then enter any of them? I also get a prompt saying this password is not transferred “safely” (I assume plain text rather than encrypted) – is there some way around this (does not sound very safe)?
I am having the same issue with the screen not letting me login. It is a bug that that is being tracked on centos as well as red hat. ‘https://bugs.centos.org/view.php?id=16572#history’
As for the dual login. The first login is just to get in through VNC, the second login is actually the login of the screen saver for the user you are logging in as.
I hope this gets fixed as the system is not usable as a report desktop without it.
How can I set the display resolution?
Is there an update to install VNc WITH selinux at ON. ? Quite better than removing it.. Thanks
VNC works and I can see the desktop and interact with it, but if I try to open Terminal it opens on the VM screen, but not on my VNC. If I load Firefox it opens on my VNC screen but not my VM. It’s strange. Any ideas?
Hello!
this tutorial works but when I want to connect there is blank screen. In log files there are no errors.
Hello!
I’ve got the same result – blank black screen after typing VNC password.
Any suggestions here?
me too. I’ve experience this several times, why again?… ahg..
Hi Alik and Mitja,
I found that the following /etc/systemd/system/[email protected] file entries fix the blank screen error. Change the file to the following;
Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l -c “/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1280×1024”
PIDFile=/home//.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
This works on Centos 8.1.
Correction (the file details do not render properly when you use “” to delimit username.
Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l pkumar -c “/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1280×1024”
PIDFile=/home/pkumar/.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c ‘/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :’
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target