KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is an open source full virtualization solution for Linux like systems, KVM provides virtualization functionality using the virtualization extensions like Intel VT or AMD-V. Whenever we install KVM on any linux box then it turns it into the hyervisor by loading the kernel modules like kvm-intel.ko( for intel based machines) and kvm-amd.ko ( for amd based machines).
KVM allows us to install and run multiple virtual machines (Windows & Linux). We can create and manage KVM based virtual machines either via virt-manager graphical user interface or virt-install & virsh cli commands.
In this article we will discuss how to install and configure KVM hypervisor on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server. I am assuming you have already installed Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server on your system. Login to your server and perform the following steps.
Step:1 Verify Whether your system support hardware virtualization
Execute below egrep command to verify whether your system supports hardware virtualization or not,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo 1 linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$
If the output is greater than 0 then it means your system supports Virtualization else reboot your system, then go to BIOS settings and enable VT technology.
Now Install “kvm-ok” utility using below command, it is used to determine if your server is capable of running hardware accelerated KVM virtual machines
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo apt install cpu-checker
Run kvm-ok command and verify the output,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo kvm-ok INFO: /dev/kvm exists KVM acceleration can be used linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$
Step:2 Install KVM and its required packages
Run the below apt commands to install KVM and its dependencies
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo apt update linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo apt install qemu qemu-kvm libvirt-bin bridge-utils virt-manager
Once the above packages are installed successfully, then your local user (In my case linuxtechi) will be added to the group libvirtd automatically.
Step:3 Start & enable libvirtd service
Whenever we install qemu & libvirtd packages in Ubuntu 18.04 Server then it will automatically start and enable libvirtd service, In case libvirtd service is not started and enabled then run beneath commands,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo service libvirtd start linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo update-rc.d libvirtd enable
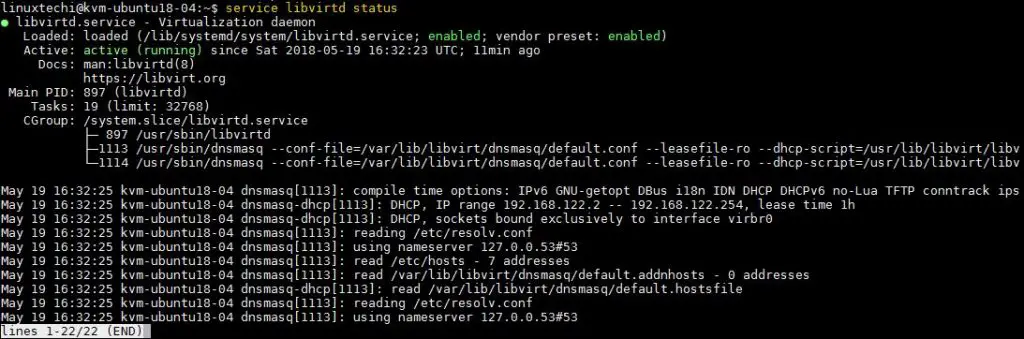
Now verify the status of libvirtd service using below command,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ service libvirtd status
Output would be something like below:
Step:4 Configure Network Bridge for KVM virtual Machines
Network bridge is required to access the KVM based virtual machines outside the KVM hypervisor or host. In Ubuntu 18.04, network is managed by netplan utility, whenever we freshly installed Ubuntu 18.04 server then netplan file is created under /etc/netplan/. In most of the hardware and virtualized environment, netplan file name would be “50-cloud-init.yaml” or “01-netcfg.yaml”, to configure static IP and bridge, netplan utility will refer this file.
As of now I have already configured the static IP via this file and content of this file is below:
network: ethernets: ens33: addresses: [192.168.0.51/24] gateway4: 192.168.0.1 nameservers: addresses: [192.168.0.1] dhcp4: no optional: true version: 2
Let’s add the network bridge definition in this file,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo vi /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
network: version: 2 ethernets: ens33: dhcp4: no dhcp6: no bridges: br0: interfaces: [ens33] dhcp4: no addresses: [192.168.0.51/24] gateway4: 192.168.0.1 nameservers: addresses: [192.168.0.1]
As you can see we have removed the IP address from interface(ens33) and add the same IP to the bridge ‘br0‘ and also added interface (ens33) to the bridge br0. Apply these changes using below netplan command,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo netplan apply linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$
If you want to see the debug logs then use the below command,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo netplan --debug apply
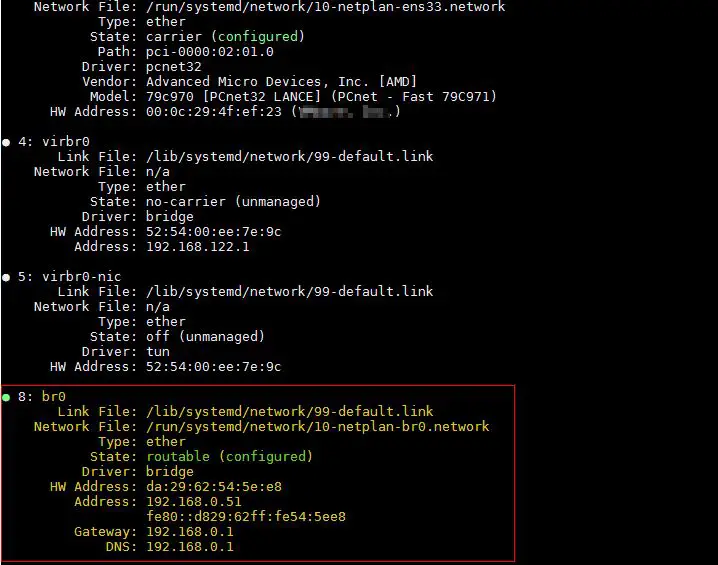
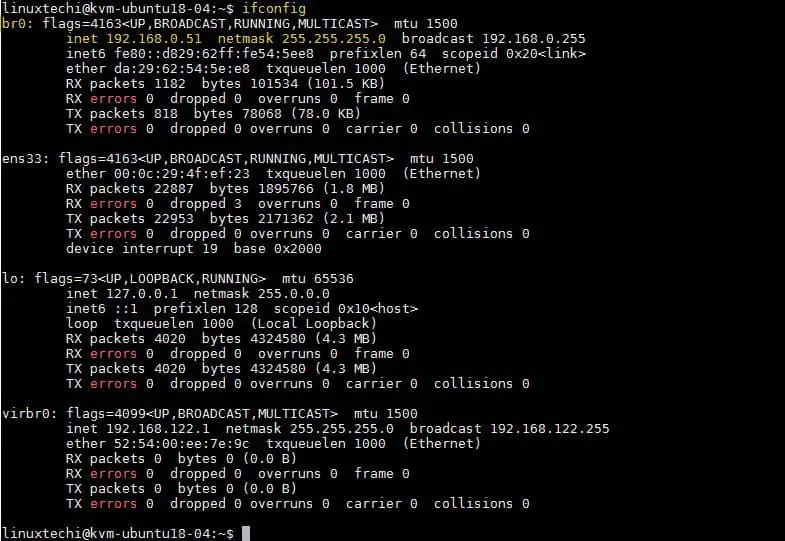
Now Verify the bridge status using following methods:
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo networkctl status -a
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ ifconfig
Start:5 Creating Virtual machine (virt-manager or virt-install command )
There are two ways to create virtual machine:
- virt-manager (GUI utility)
- virt-install command (cli utility)
Creating Virtual machine using virt-manager:
Start the virt-manager by executing the beneath command,
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo virt-manager
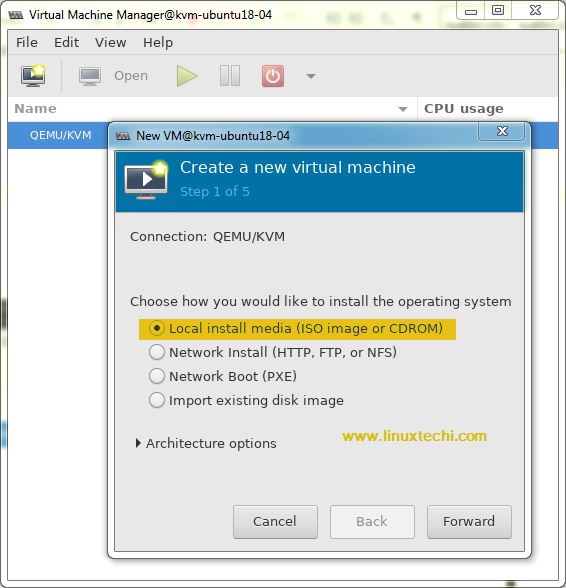
Create a new virtual machine
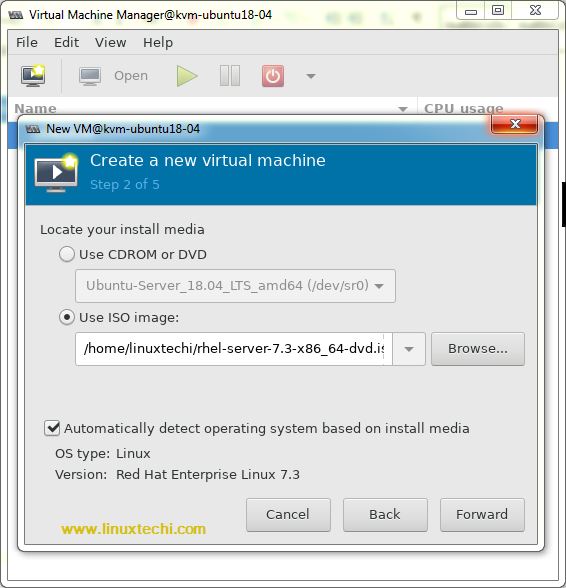
Click on forward and select the ISO file, in my case I am using RHEL 7.3 iso file.
Click on Forward
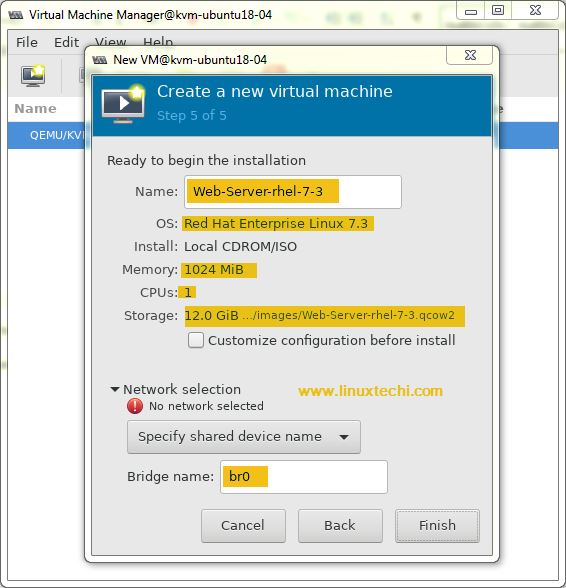
In the next couple of windows, you will be prompted to specify the RAM, CPU and disk for the VM.
Now Specify the Name of the Virtual Machine and network,
Click on Finish
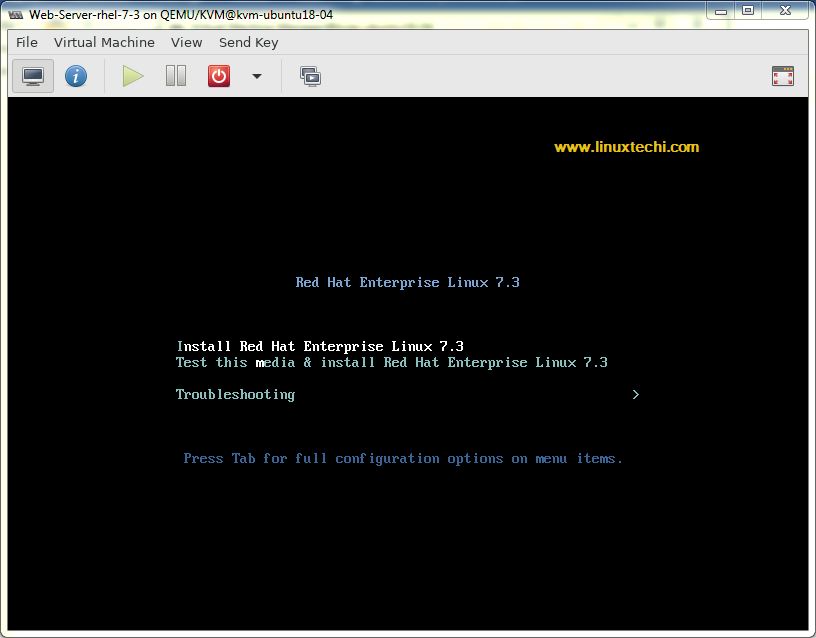
Now follow the screen instruction and complete the installation,
Read More On : “How to Create, Revert and Delete KVM Virtual machine (domain) snapshot with virsh command”
Creating Virtual machine from CLI using virt-install command,
Use the below virt-install command to create a VM from terminal, it will start the installation in CLI, replace the name of the VM, description, location of ISO file and network bridge as per your setup.
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo virt-install -n DB-Server --description "Test VM for Database" --os-type=Linux --os-variant=rhel7 --ram=1096 --vcpus=1 --disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/dbserver.img,bus=virtio,size=10 --network bridge:br0 --graphics none --location /home/linuxtechi/rhel-server-7.3-x86_64-dvd.iso --extra-args console=ttyS0
That’s conclude the article, I hope this article help you to install KVM on your Ubuntu 18.04 Server. Apart from this, KVM is the default hypervisor for Openstack.
Read More on : How to Install and Configure KVM on OpenSUSE Leap 15


To check virtualization support the command should be …
egrep -c ‘(vmx|svm)’ /proc/cpuinfo
You are the best thank you very much, better than on the manufacturer’s website 🙂
Do I understand correctly from Step 5 that one can be logged into a headless U 18.04 server via ssh and run the graphical virt-manager utility? Even in the absence of a local graphical environment?
If so, how must ssh be configured? Is it just a question of setting X11Forwarding=yes in the respective ssh_config and sshd_config files?
You’ll also need to install a X server on your host machine (for Windows, I recommend vcxsrv, open source and updated).
Doc states:
whenever we freshly installed Ubuntu 18.04 server then a file with name “/etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml” is created automatically, to configure static IP and bridge, netplan utility will refer this file.
NOT TRUE, this file is missing.
Would be helpful if based on ifconfig output how this file could be created
Hi Eddie,
In case netplan is not present in your server then i would recommend create a file with name “01-netcfg.yaml” under /etc/netplan directory and copy paste the contents from article to this file.
Great article, step by step very helpful^_^ Thanks