HAProxy stands for High Availability Proxy, it is a free and open source load balancer tool which allow to balance the incoming traffic (TCP and HTTP based) by distributing across the backend servers using different criteria.
In other words, we can say HAProxy is used to provide fault tolerance and high availability in case when one node is getting too many concurrent requests. It is used by most famous web sites like GitHub, Stack Overflow and Tumbler.
In this article, we will discuss how to install and configure HAProxy on CentOS 8/RHEL 8 for Nginx Web Servers. Following are the details for my haproxy lab setup,
- HAProxy Server – 192.168.1.10 (haproxy-centos8)
- Nginx Server 1 – 192.168.1.11 (nginx-node01)
- Nginx Server 2 – 192.168.1.12 (nginx-node01)
Let’s jump into installation and configuration steps of HAProxy on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Step:1) Update /etc/hosts file of your HAProxy Server
Login to your CentOS 8 or RHEL 8 system where you will install haproxy, add the following lines in /etc/hosts file,
192.168.1.10 haproxy-centos8 192.168.1.11 nginx-node01 192.168.1.12 nginx-node02
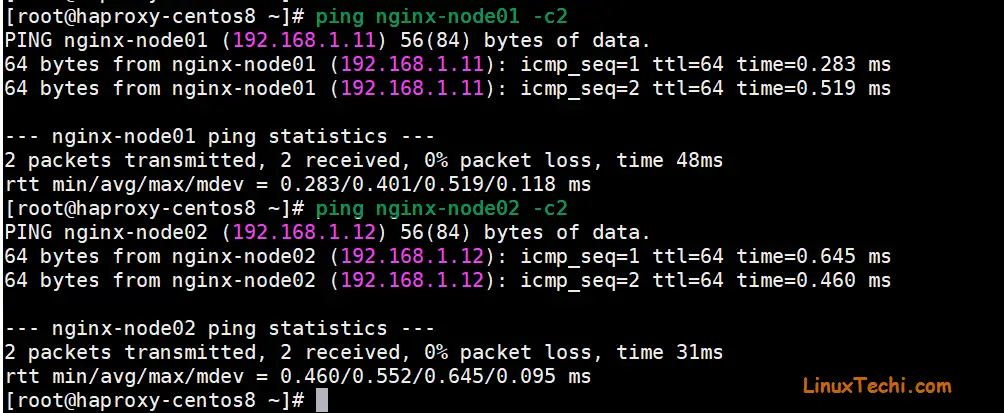
After updating the hosts file, make sure you are able to ping Nginx nodes,
Step:2) Install and Configure HAProxy on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8
Haproxy package is available in the default package repositories of CentOS 8 and RHEL 8, so it can be easily installed with dnf command. But it is recommended update your system before installing haproxy. So execute the following command,
root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# dnf update -y root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# reboot
Now use following dnf command to install haproxy,
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# dnf install haproxy
Once the haproxy is installed successfully, configure it by editing its configuration file “/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg“.
Before editing the file, it is always a good practice to make a backup of original file , run the following command,
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# cd /etc/haproxy/ [root@haproxy-centos8 haproxy]# cp haproxy.cfg haproxy.cfg-org [root@haproxy-centos8 haproxy]#
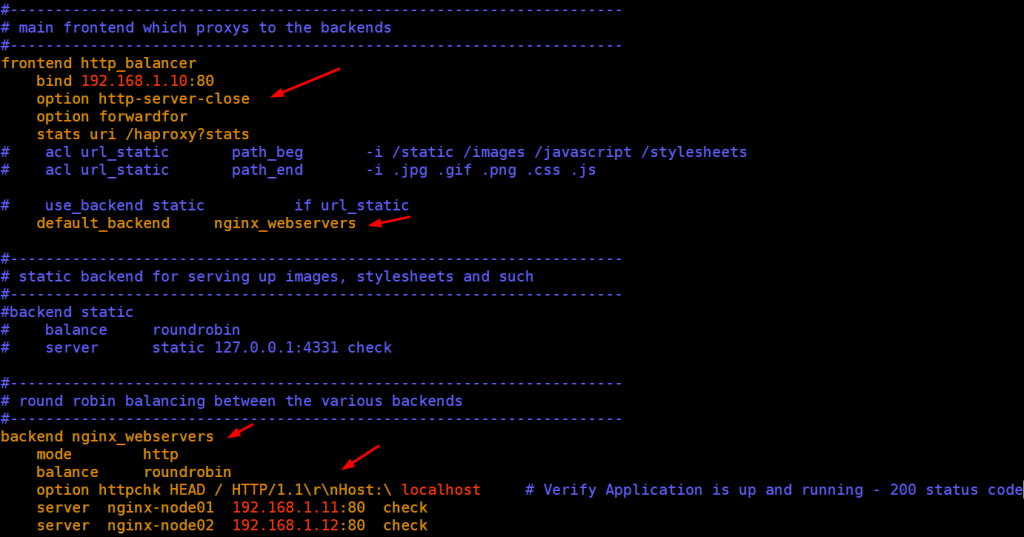
In configuration file, we will modify two sections frontend and backend. In Frontend section we define the haproxy IP and its port, stats uri and backend name. In Backend section we define the type of load balance algorithm we will use like round robin & least connection etc and backend server’s name, IPs and port, example is demonstrated below,
[root@haproxy-centos8 haproxy]# vi haproxy.cfg ………………… frontend http_balancer bind 192.168.1.10:80 option http-server-close option forwardfor stats uri /haproxy?stats # acl url_static path_beg -i /static /images /javascript /stylesheets # acl url_static path_end -i .jpg .gif .png .css .js # use_backend static if url_static default_backend nginx_webservers backend nginx_webservers mode http balance roundrobin option httpchk HEAD / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost:\ localhost server nginx-node01 192.168.1.11:80 check server nginx-node02 192.168.1.12:80 check ………………………………
Save and exit the file
Configure rsyslog so that it stores all HAProxy statistics, edit rsyslog config file “/etc/rsyslog.conf” and uncomment line 19 and 20,
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# vi /etc/rsyslog.conf …… module(load="imudp") input(type="imudp" port="514") ……
Save and exit the file.
Now create haproxy.conf file for rsyslog , paste the following lines,
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# vi /etc/rsyslog.d/haproxy.conf local2.=info /var/log/haproxy-access.log local2.notice /var/log/haproxy-info.log
save and exit the file
Restart and enable rsyslog service so that it will be available across the reboots
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog [root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# systemctl enable rsyslog
Now finally start haproxy but before starting haproxy service, set the following selinux rule,
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# setsebool -P haproxy_connect_any 1
Start & enable haproxy using beneath systemctl commands
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# systemctl start haproxy [root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# systemctl enable haproxy
Allow the haproxy port (in our case it is 80) in OS firewall, execute the beneath firewall-cmd command,
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp [root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
Till now HAProxy installation and configuration part is completed let’s move to Nginx nodes,
Step:3) Install NGINX and start its service
Login to both nginx nodes, install nginx and start its service using the following commands.
# dnf install nginx -y # systemctl start nginx # systemctl enable nginx
Let’s modify the index.html file of respective node,
For nginx-node01
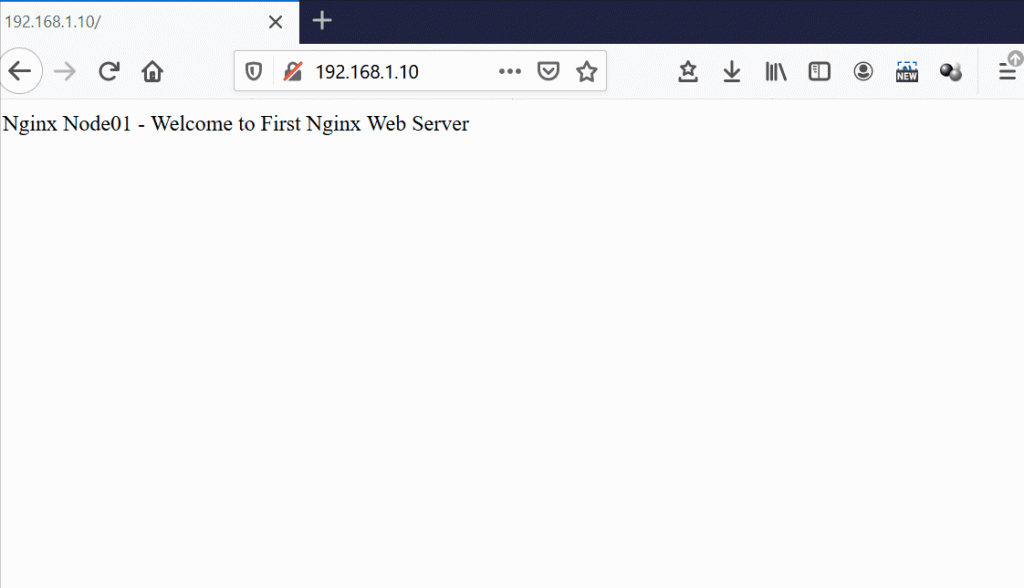
[root@nginx-node01 ~]# cd /usr/share/nginx/html [root@nginx-node01 html]# echo "Nginx Node01 - Welcome to First Nginx Web Server" > index.html
For nginx-node02
[root@nginx-node02 ~]# cd /usr/share/nginx/html [root@nginx-node02 html]# echo "Nginx Node02 - Welcome to 2nd Nginx Web Server" > index.html
Allow Nginx port (80) in the OS firewall in both nodes using below command,
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http # firewall-cmd --reload
Step:4) Test Whether Your HAProxy is working properly or not
Login to haproxy server and run the curl command couple of times to see whether traffic is distributed in round-robin way
[root@haproxy-centos8 ~]# curl 192.168.1.10
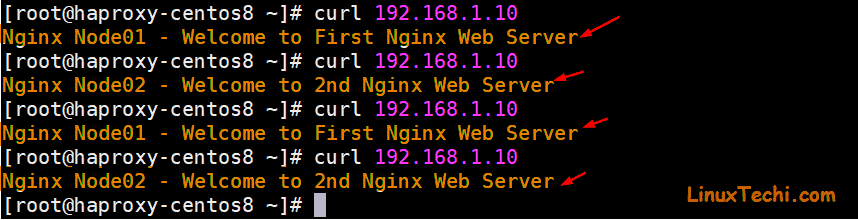
Perfect, this confirms haproxy is working properly as it is distributing traffic between two nodes,
Let’s verify from the Web browser too,
Above confirms that HAProxy has configured successfully on CentOS 8 and RHEL 8.
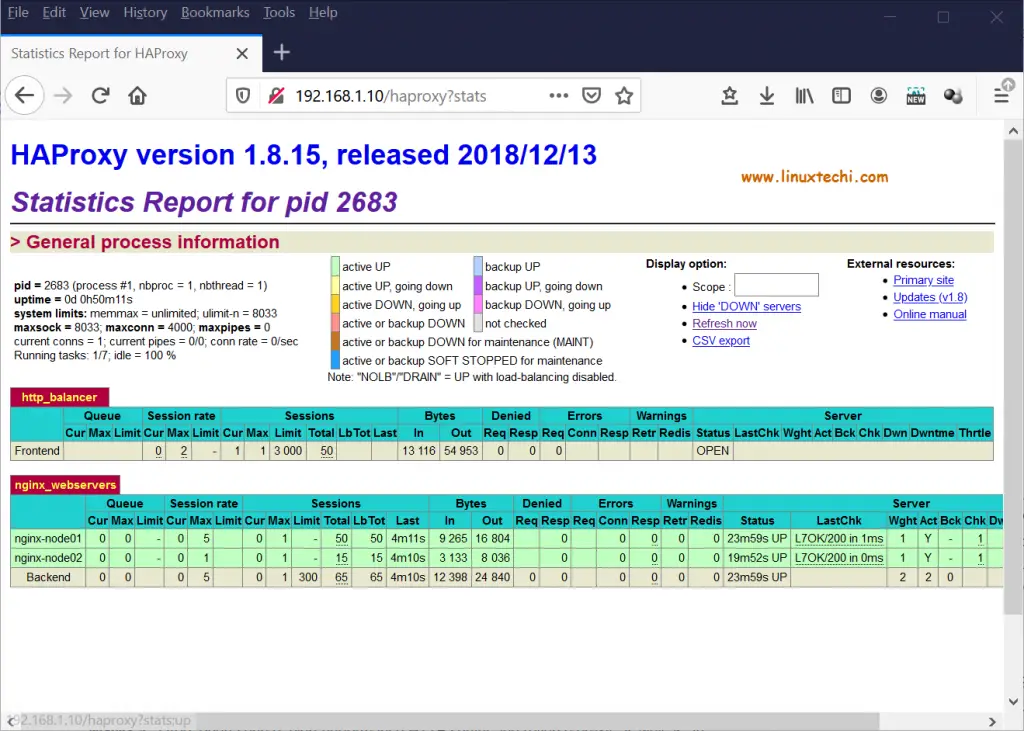
You can view the status of your haproxy via web browser, type url : http://<HA-Proxy-IP>/haproxy?stats
In our case URL will be http://192.168.1.10/haproxy?stats
We can also view HAProxy statistics from log file ( /var/log/haproxy-access.log).
That’s all from this tutorial, I hope these steps help you to setup HAProxy on CentOS 8 and RHEL 8 smoothly. Please do share your valuable feedback and comments.


Nice and very clear tutoria, thanks for sharing it.
How to apply fixes?
1.8.23 -> 1.8.28
How to update version?
1.8.23 -> 2.2.8
Can you explain how to make haproxy highly available so that you don’t have a single point of failure?
Hi Mauricio,
You can configure highly available haproxy using keepalived.