In this guide, we will explain how to setup SFTP server on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS system step-by-step.
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) is a secure and reliable method for transferring files between systems over a network. Setting up an SFTP server on Linux allows you to securely transfer files, manage permissions, and control access.
Background of SFTP & chroot :
SFTP stands for SSH File Transfer protocol or Secure File Transfer Protocol. SFTP provides file access, file transfer, and file management functionalities over any reliable data stream. When we configure SFTP in chroot environment , then only allowed users will be limited to their home directory , or we can say allowed users will be in jail like environment where they can’t even change their directory.
Prerequisites
- Pre Install Ubuntu 24.04 Instance
- Local with sudo rights
- Basic knowledge of Linux command-line operations.
- Internet connectivity or locally configured repository.
How to Setup SFTP Server on Ubuntu 24.04
Without any delay, let’s jump into SFTP Server installation and configurations steps. Refer the following steps one after the another.
1) Install OpenSSH Server
SFTP is a part of the OpenSSH package,so install openssh server package on your Ubuntu system. If it is already installed then you skip this step.
Open the terminal, run the following commands:
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install openssh-server -y
Once openssh server installed, start and enable it’s service using following systemctl commands.
$ sudo systemctl start sshd $ sudo systemctl enable sshd
2) Create SFTP Group and User
To manage access to the SFTP server, it is a good practice to create a dedicated SFTP group and user.
Create a sftp_users group using groupadd command:
$ sudo groupadd sftp_users
Add a new user and assign it to the sftp_users group. This user will only have SFTP access:
$ sudo useradd -m -G sftp_users -s /usr/sbin/nologin sftpuser
In above command, ‘-s /usr/sbin/nologin‘ option ensures that the user cannot log in via SSH and can only use SFTP.
Next, set a password for the new SFTP user, run passwd command
$ sudo passwd sftpuserNew password: Retype new password: passwd: password updated successfully $
3) Configure SSH for SFTP-Only Access
Now, we need to configure SSH to restrict the SFTP users to SFTP-only access. Edit sshd_config file using your favorite editor, add the following lines at the end of the file to configure SFTP-only access for users in the sftp_users group:
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config #comment out the below line and add a line like below #Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server Subsystem sftp internal-sftp # add Below lines at the end of file Match Group sftp_users ChrootDirectory %h ForceCommand internal-sftp AllowTcpForwarding no X11Forwarding no
Where :
Match Group sftp_users – This indicates that the following lines will be matched only for users who belong to group sftp_users
ChrootDirectory %h – This is the path(default user’s home directory) that will be used for chroot after the user is authenticated. So, for sftpuser, this will be /home/sftpuser
ForceCommand internal-sftp – This forces the execution of the internal-sftp and ignores any command that are mentioned in the ~/.ssh/rc file.
After making the above changes, restart the ssh service using following command,
$ sudo systemctl restart sshd // For RHEL based Distributions $ sudo systemctl restart ssh // For Debian based Distributions
4) Set the required permissions
Adjust the permissions of the user’s home directory using chown and chmod commands.
$ sudo chown root:root /home/sftpuser $ sudo chmod 755 /home/sftpuser
Create a directory where the sftpuser can upload files,
$ sudo mkdir /home/sftpuser/uploads $ sudo chown sftpuser:sftp_users /home/sftpuser/uploads
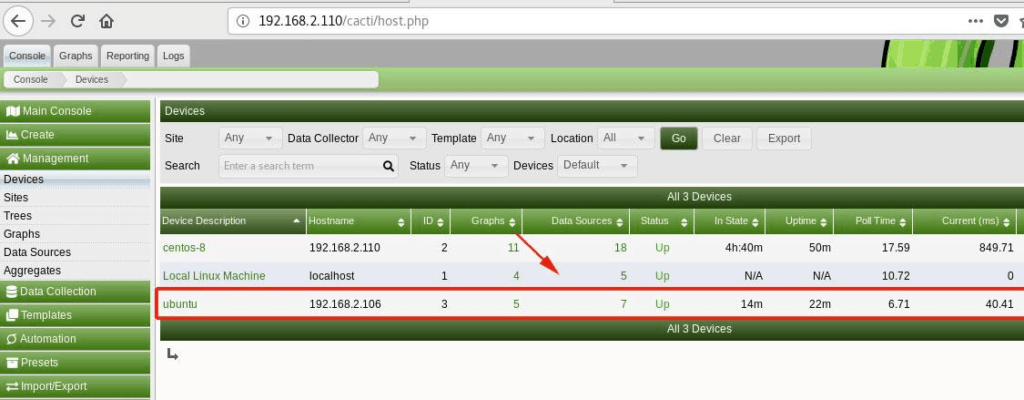
5) Test Sftp server
First try to access the system using ssh.
$ ssh sftpuser@your_server_ip
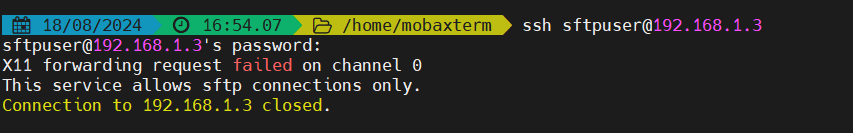
As we can see in output above sftpuser is not allowed to ssh.
Now let’s try to login using sftp,

As you can see above, sftpuser is logged in via sftp and but can’t change the directory because of chroot environment.
Now do the uploading and downloading testing as shown below:
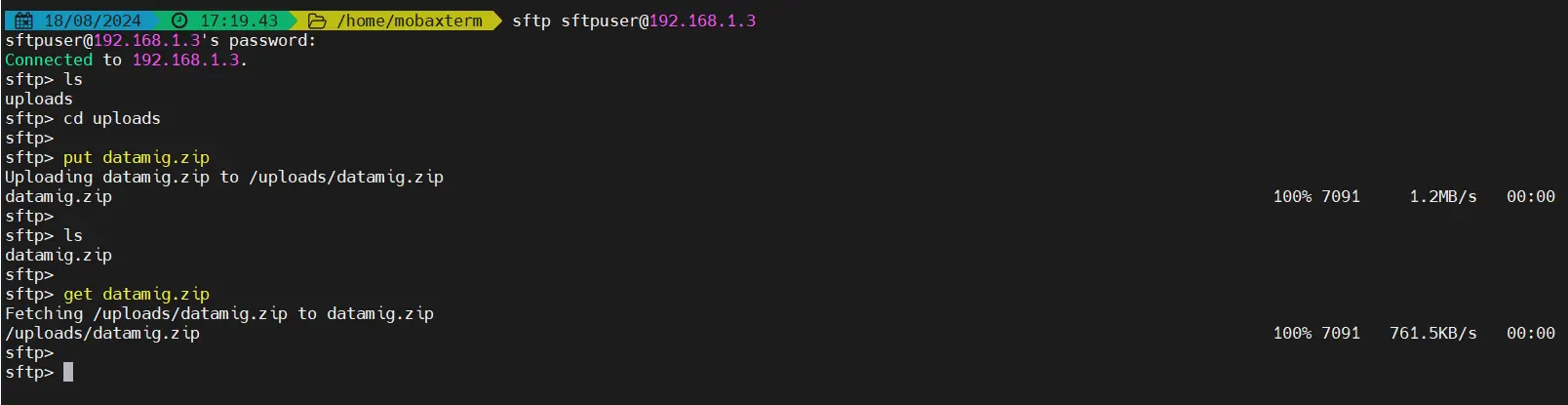
As we can see above , both uploading & downloading working fine for sftpuser user. That’s all from this guide, We hope you are able to setup sftp server on Ubuntu 24.04 using above steps.You are most welcome to share your feedback and queries in the comments sections below.
Also Read: How to Install AWS CLI on Linux Step-by-Step

I like sftp much better than regular FTP. Main reason, you can exchange keys for user that use SFTP so there are no passwords. This improves security on your server!!!
What does your personal preference of sftp over ftp have to do with the instructions provided above?
I have followed the exact steps given in the tutorial, but I am getting error in uploading a file. I am able to downlaod any files.
sftp> put sftp_file
Uploading sftp_file to /upload/sftp_file
remote open(“/upload/sftp_file”): Permission denied
sftp>
Is SELinux need to be configured anyway?
Hi Gopal ,
If Selinux is enable on your linux box , then for Chroot SFTP you need to write SELiux rule “setsebool -P ssh_chroot_rw_homedirs on”.
I hope this might help you.
Following the same exact instructions In ubuntu 14.04 I got an error after entering the password when invoking ssh wstest@localhost : Write failed broken pipe
Hi ,
These steps are tested on CentOS 6.X and RHEL 6.X , i am not sure whether these steps will work on Ubuntu Linux.
I usually see this error when I don’t have ‘root’ set as the owner & group and 755 for permissions of the user’s directory (‘Jack’ in the author’s example).
This line needs some improvement
[root@localhost jack]# chown jack. /home/jack upload/
1) All the commands above have absolute directory paths. This command make assumption that it’s in the directory /home.
2) There is a . DOT after jack ? Either a typo or means current directory. See 1.
3) Why upload/ is this just upload or /home/jack/upload ?
[root@localhost jack]# cd /home/jack ; chown jack $PWD /home/jack/upload
Hi Fred ,
I have used . DOT after jack in chown command because i want to make this user both File Owner and Group Owner of upload folder. I have choose upload folder because i want jack user to upload its files and directory on upload directory only.
I’ve gone through this step by step, but when I try to log in using WinSCP, I get “Error listing directory ‘/upload’ Permission denied.
Error code: 3
Error message from server: Permission denied
Request code: 11
I can go into the folder, but I can’t list anything, and when I try to upload a file I get Permission denied.
Error code: 3
Error message from server: Permission denied
Request code: 3
Okay, when I put SELinux in Permissive mode, it works. I’m running CentOS 6, and I tried your setsebool -P ssh_chroot_rw_homedirs on but it didn’t work.
Sorry for the multiple posts
These instructions WILL NOT work for Ubuntu Linux and you will effectively lock yourself (admin/root) out if working remotely.
This solve problem with permission denide on enabled selinux:
setsebool -P ssh_chroot_full_access on
Very well explained and written. This is very helpful.