In this tutorial, we will show you how to Automount NFS share in Linux using Autofs.
Network File System (NFS) is a robust way to share directories across systems, enabling seamless access to files. However, manually mounting NFS shares can be tedious, especially when managing multiple systems. This is where autofs, a dynamic automounting tool, shines. Autofs automatically mounts NFS shares when accessed and unmounts them when idle, saving system resources.
Prerequisites
- A working NFS server with shared directories.
- A Linux client machine (tested on Debian 12, RHEL 9).
- Sudo or root access on the client machine.
Autofs service reads two files Master map file ( /etc/auto.master ) and a map file like /etc/auto.misc or /etc/auto.xxxx.
In ‘/etc/auto.master’ file we have three different fields :
/<Mount-Point> <Map-file> <Timeout-Value>
In map file (/etc/auto.misc or /etc/auto.xxxx) also we have three different fields:
<Mount-Point> <Mount-Options> <Location_of_File System>
In this tutorial, we will demonstrate how to mount an NFS share using autofs. The NFS share /var/nfs_share is exported from an Ubuntu 24.04 NFS server with the IP address 192.168.1.11. We will mount this NFS share on both RHEL 9 and Debian 12 or Ubuntu 24.04 Linux systems using autofs.
Mount nfs share using Autofs in RHEL 9
1) Install autofs package
Install the autofs package using below yum command if it is not installed.
$ sudo rpm -q autofs package autofs is not installed $ sudo dnf install autofs
2) Edit the Master map file (/etc/auto.master )
Add the following line .
$ sudo vi /etc/auto.master /dbstuff /etc/auto.nfsdb --timeout=180
Note : Mount point ‘/dbstuff’‘ must exist on your system. If not then create a directory ‘mkdir /dbstuff‘. NFS Share will automatically umount after 180 seconds or 3 minutes if don’t perform any action on the share.
3) Create a map file ‘/etc/auto.nfsdb’
Create a map file and add the following line.
$ sudo vi /etc/auto.nfsdb db_backup -fstype=nfs,rw,soft,intr 192.168.1.11:/var/nfs_share
Save and exit the file.
Where :
- db_backup is a mount point.
- -fstype=nfs is the file system type & ‘rw,soft,intr’ are mount options.
- ‘192.168.1.11:/var/nfs_share’ is nfs share location.
4) Start the auotfs service
$ sudo systemctl restart autofs.service $ sudo systemctl enable autofs.service
5) Try to access the mount point
Mount point of nfs share will be ‘/dbstuff/db_backup‘. When we try access the mount point then autofs service will mount nfs share automatically as shown below:
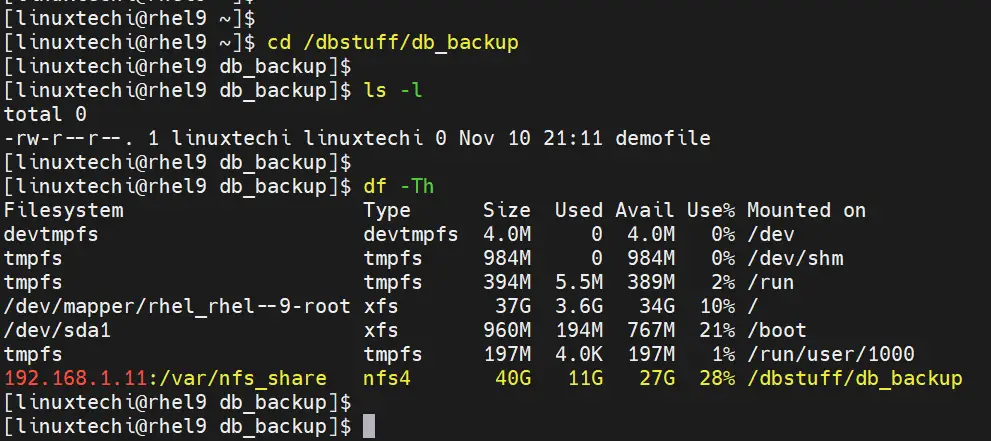
Mount NFS share using autofs in Debian 12 / Ubuntu 24.04
1) Install the autofs package using apt command
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt install autofs -y
2) Edit the Master Map file ‘/etc/auto.master’
Add the following line in the master map file.
$ sudo vi /etc/auto.master /dbstuff /etc/auto.nfsdb --timeout=180
Save & exit the file.
Create the mount point.
$ sudo mkdir /dbstuff
3) Create a map file ‘/etc/auto.nfsdb’
Add the following line in the map file.
$ sudo vi /etc/auto.nfsdb db_backup -fstype=nfs4,rw,soft,intr 192.168.1.11:/var/nfs_share
4) Start the autofs service
$ sudo systemctl restart autofs && sudo systemctl enable autofs
5) Try to access the mount point
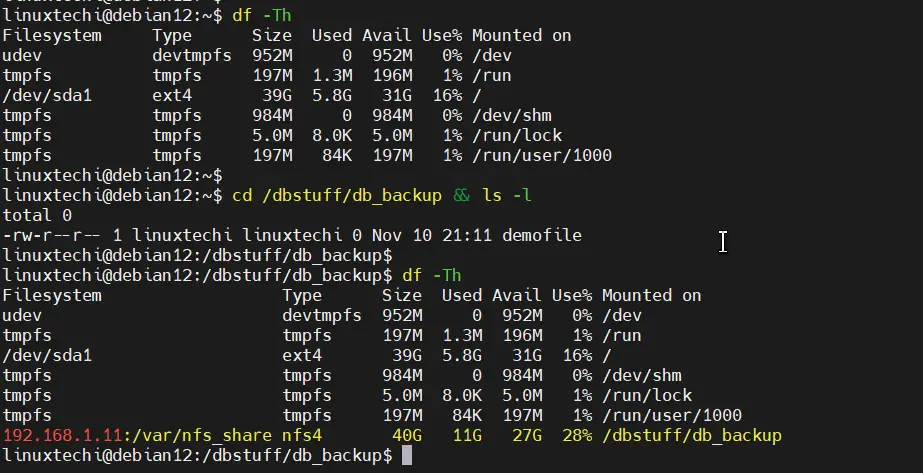
Perfect, above confirms that NFS share has been mount automatically via autofs.
That’s all from tutorial, I hope you have found it useful and informative, feel free to post your queries and feedback in below comments section.


Centos7 has systemd with automount. Thus you don’t really need autofs.
How to create multiple automount in nfs
@pramod: I think you need to add in /etc/auto.nfsdb file otherwise you can use RHEL IDM , FreeIPA to manage automount in your environment.
How to list all autofs mount points in command line
mount | grep autofsThis command lists all currently mounted autofs directories.